ГОСУДАРСТВЕННЫЙ СТАНДАРТ РЕСПУБЛИКИ БЕЛАРУСЬ
КАНАТЫ ПРОВОЛОЧНЫЕ СТАЛЬНЫЕ. БЕЗОПАСНОСТЬ
Часть 2
Термины и определения, обозначения и классификация
КАНАТЫ ДРАЦЯНЫЯ СТАЛЬНЫЯ. БЯСПЕКА
Частка 2
Тэрмшы i азначэнш, абазначэнш i клас1ф1кацыя
(EN 12385-2:2002, ЮТ)
Издание официальное
(пВ
СТБ EN 12385-2-2009
УДК 669.14-427.4:001.4(083.74X476) МКС 01.040.77; 77.140.65 КП 03 ЮТ
Ключевые слова: канаты стальные, безопасность, термины, классификация
Предисловие
Цели, основные принципы, положения по государственному регулированию и управлению в области технического нормирования и стандартизации установлены Законом Республики Беларусь «О техническом нормировании и стандартизации».
1 ПОДГОТОВЛЕН ПО УСКОРЕННОЙ ПРОЦЕДУРЕ научно-производственным республиканским унитарным предприятием «Белорусский государственный институт стандартизации и сертификации» (БелГИСС)
ВНЕСЕН Госстандартом Республики Беларусь
2 УТВЕРЖДЕН И ВВЕДЕН В ДЕЙСТВИЕ постановлением Госстандарта Республики Беларусь от 4 декабря 2009 г. № 65
3 Настоящий стандарт идентичен европейскому стандарту EN 12385-2:2002 + А1:2008 Steel wire ropes. Safety. Part 2. Definitions, designations and classifications (Канаты проволочные стальные. Безопасность. Часть 2. Термины и определения).
Европейский стандарт разработан техническим комитетом по стандартизации CEN/TC 168 «Цепи, канаты, подъемные полосы, стропы и принадлежности. Безопасность» Европейского комитета по стандартизации (CEN).
Перевод с английского языка (еп).
Официальные экземпляры европейского стандарта, на основе которого подготовлен настоящий государственный стандарт, и европейских стандартов, на которые даны ссылки, имеются в Национальном фонде ТИПА.
Степень соответствия - идентичная (ЮТ)
4 ВВЕДЕН ВПЕРВЫЕ
© Госстандарт, 2010
Настоящий стандарт не может быть воспроизведен, тиражирован и распространен в качестве официального издания без разрешения Госстандарта Республики Беларусь
Издан на русском языке
СТБ EN 12385-2-2009
3.4.3
preservation agent
a material, usually some form of blocking compound, applied during and/or after manufacture of the rope and/or to fibre inserts and coverings for the purpose of providing protection against corrosion
3.5
Insert (I)
fibre or solid polymers so positioned as to separate adjacent strands or wires in the same or overlying layers, or fill the interstices of the rope
3.6 Rope types
3.6.1 Stranded ropes
3.6.1.1
stranded rope
an assembly of several strands laid helically in one or more layers around a core (single-layer rope) or centre (rotation-resistant or parallel-closed rope).
NOTE Stranded ropes consisting of three or four outer strands can, or cannot, have a core.
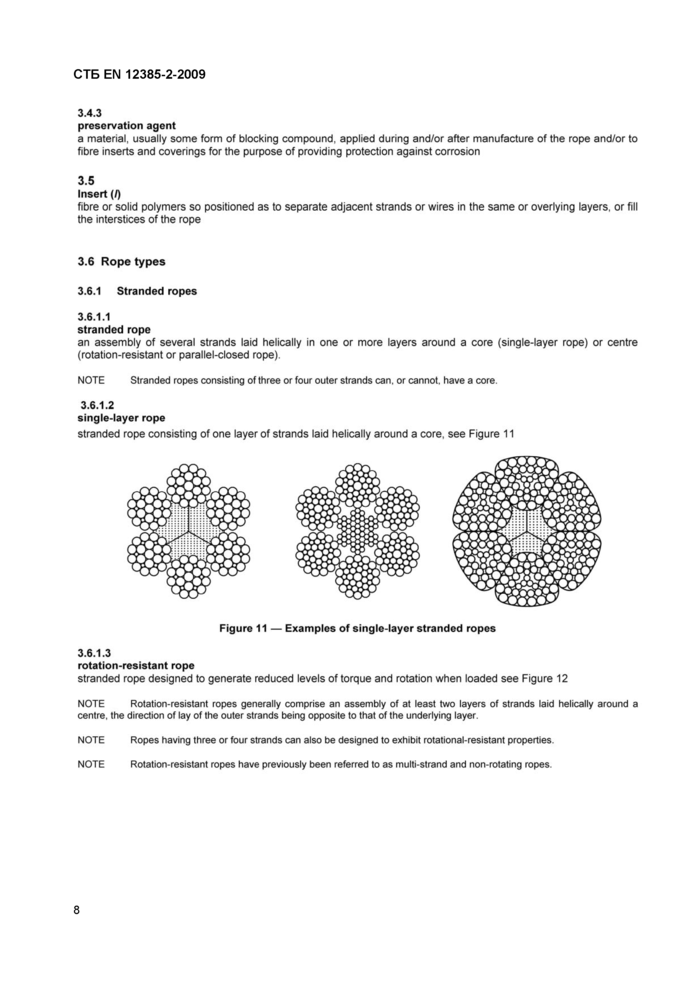
3.6.1.2
single-layer rope
stranded rope consisting of one layer of strands laid helically around a core, see Figure 11
|
|
Figure 11 — Examples of single-layer stranded ropes |
3.6.1.3
rotation-resistant rope
stranded rope designed to generate reduced levels of torque and rotation when loaded see Figure 12
NOTE Rotation-resistant ropes generally comprise an assembly of at least two layers of strands laid helically around a centre, the direction of lay of the outer strands being opposite to that of the underlying layer.
NOTE Ropes having three or four strands can also be designed to exhibit rotational-resistant properties.
NOTE Rotation-resistant ropes have previously been referred to as multi-strand and non-rotating ropes.
8
СТБ EN 12385-2-2009
|
|
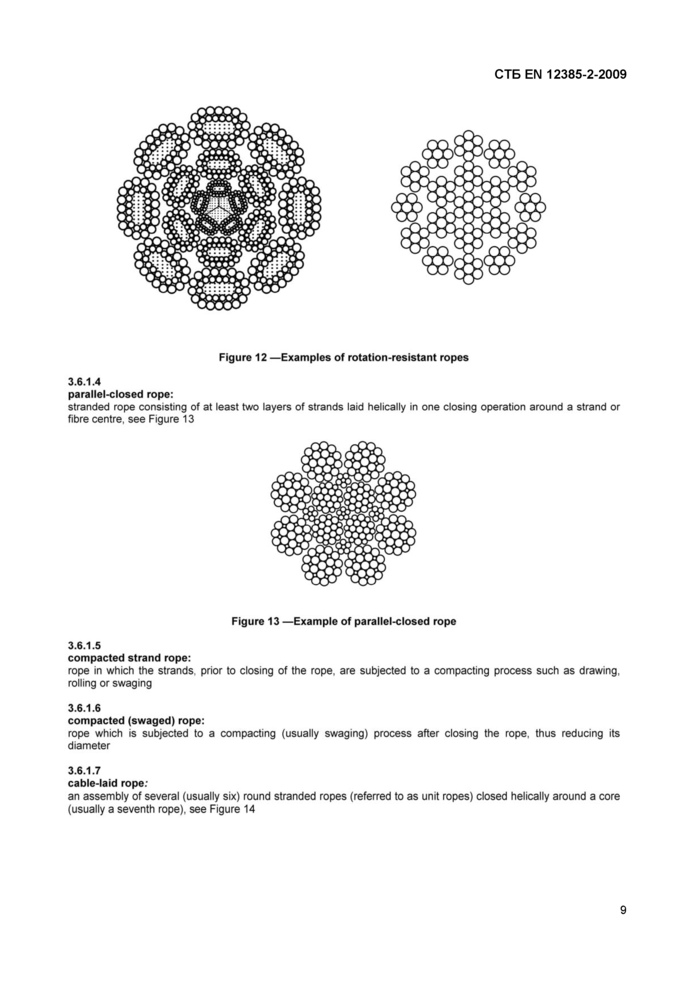
Figure 12 —Examples of rotation-resistant ropes |
3.6.1.4
parallel-closed rope:
stranded rope consisting of at least two layers of strands laid helically in one closing operation around a strand or fibre centre, see Figure 13
|
|
Figure 13 —Example of parallel-closed rope |
3.6.1.5
compacted strand rope:
rope in which the strands, prior to closing of the rope, are subjected to a compacting process such as drawing, rolling or swaging
3.6.1.6
compacted (swaged) rope:
rope which is subjected to a compacting (usually swaging) process after closing the rope, thus reducing its diameter
3.6.1.7
cable-laid rope:
an assembly of several (usually six) round stranded ropes (referred to as unit ropes) closed helically around a core (usually a seventh rope), see Figure 14
9
СТБ EN 12385-2-2009
|
|
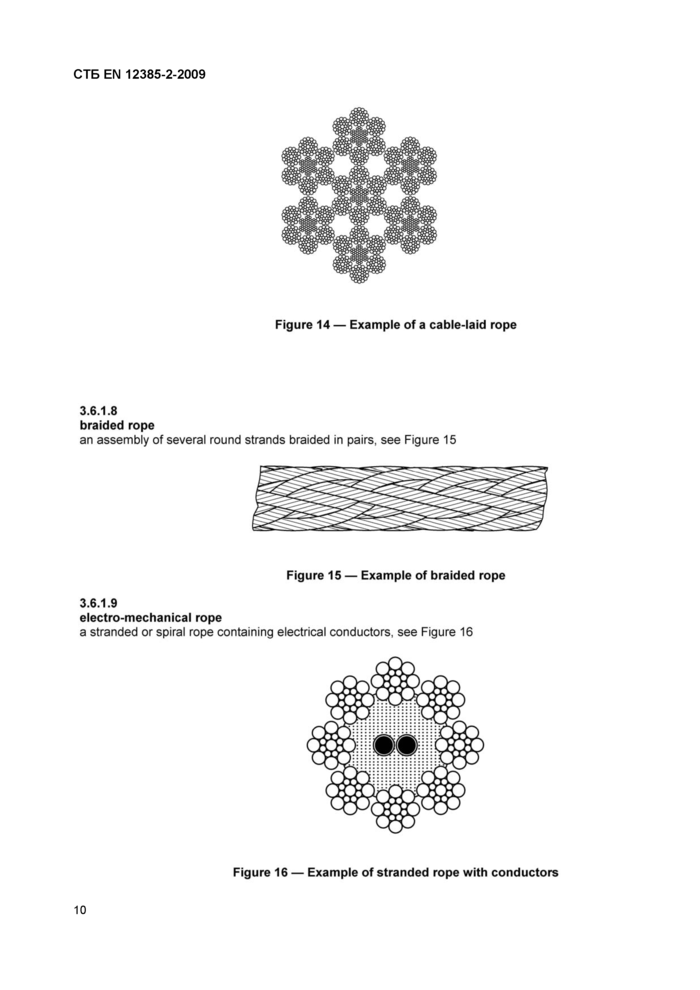
Figure 14 — Example of a cable-laid rope |
3.6.1.8 braided rope
|
|
Figure 15 — Example of braided rope |
an assembly of several round strands braided in pairs, see Figure 15
3.6.1.9
electro-mechanical rope
|
|
Figure 16 — Example of stranded rope with conductors |
a stranded or spiral rope containing electrical conductors, see Figure 16
10
СТБ EN 12385-2-2009
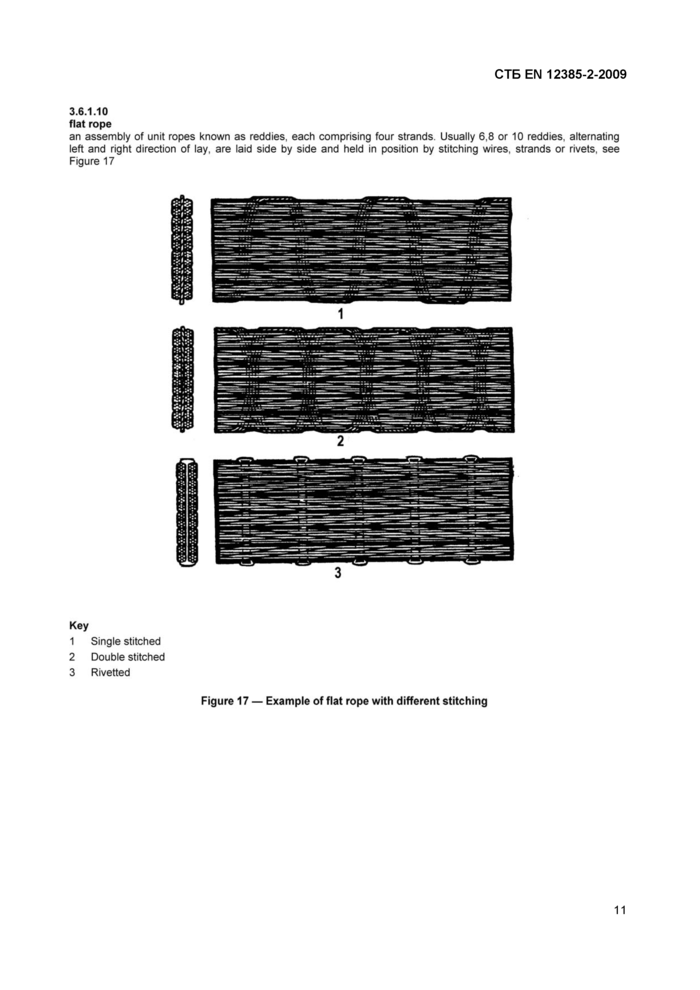
3.6.1.10
flat rope
an assembly of unit ropes known as reddies, each comprising four strands. Usually 6,8 or 10 reddies, alternating left and right direction of lay, are laid side by side and held in position by stitching wires, strands or rivets, see Figure 17
Key
1 Single stitched
2 Double stitched
3 Ri vetted
Figure 17 — Example of flat rope with different stitching
11
СТБ EN 12385-2-2009
3.6.2 Spiral ropes
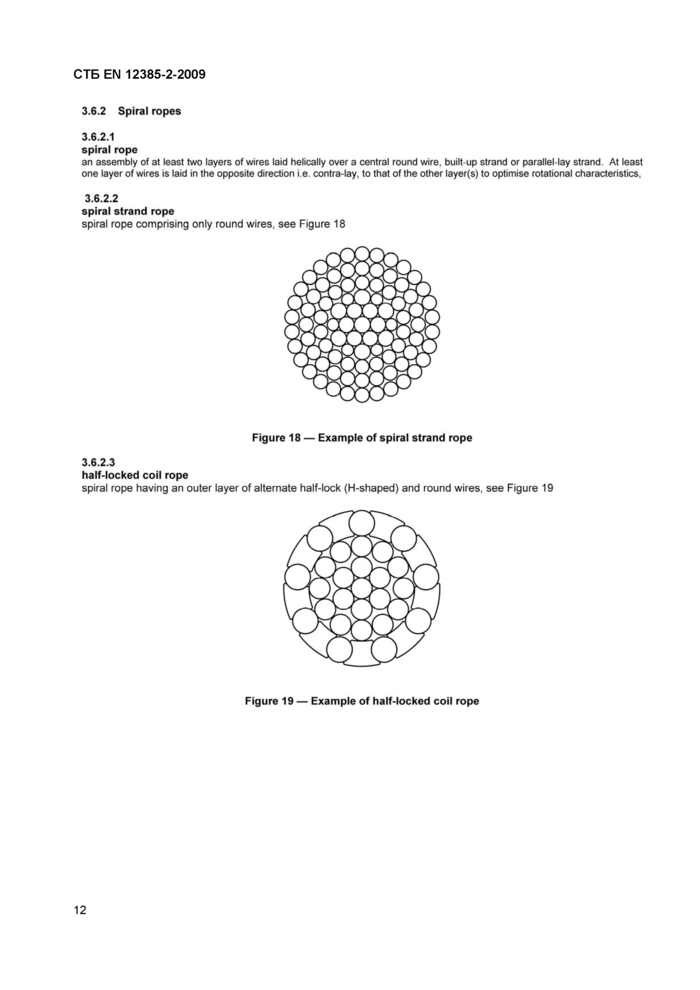
3.6.2.1 spiral rope
an assembly of at least two layers of wires laid helically over a central round wire, built-up strand or parallel-lay strand. At least one layer of wires is laid in the opposite direction i.e. contra-lay, to that of the other layer(s) to optimise rotational characteristics,
3.6.2.2
spiral strand rope
spiral rope comprising only round wires, see Figure 18
|
|
Figure 18 — Example of spiral strand rope |
3.6.2.3
half-locked coil rope
spiral rope having an outer layer of alternate half-lock (H-shaped) and round wires, see Figure 19
|
|
Figure 19 — Example of half-locked coil rope |
12
СТБ EN 12385-2-2009
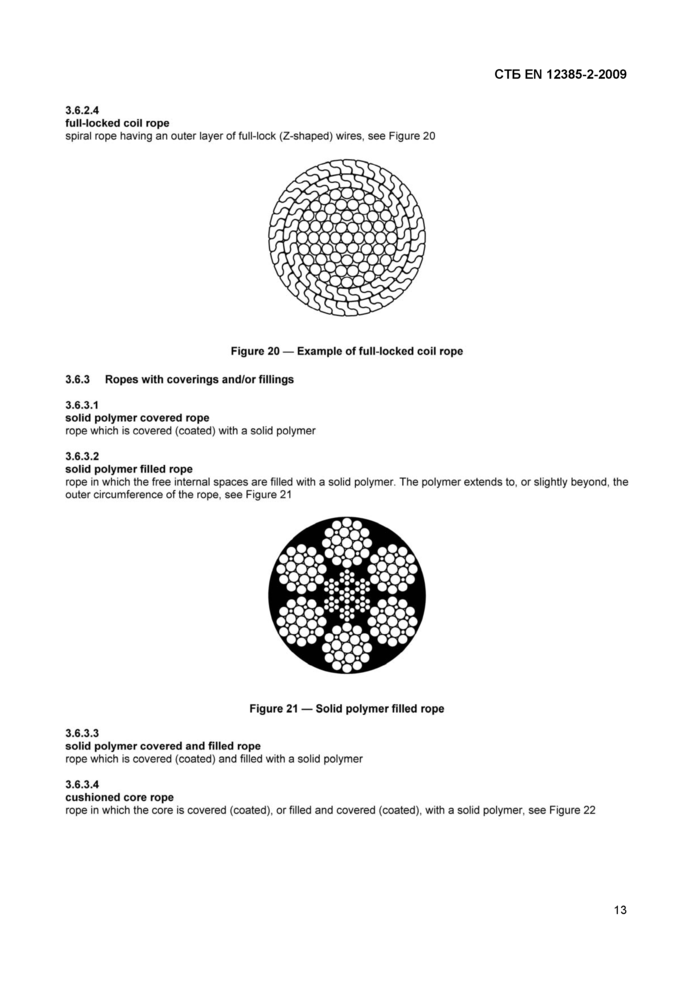
3.6.2.4
full-locked coil rope
spiral rope having an outer layer of full-lock (Z-shaped) wires, see Figure 20
Figure 20 — Example of full-locked coil rope 3.6.3 Ropes with coverings and/or fillings
3.6.3.1
solid polymer covered rope
rope which is covered (coated) with a solid polymer
3.6.3.2
solid polymer filled rope
rope in which the free internal spaces are filled with a solid polymer. The polymer extends to, or slightly beyond, the outer circumference of the rope, see Figure 21
|
|
Figure 21 — Solid polymer filled rope |
3.6.3.3
solid polymer covered and filled rope
rope which is covered (coated) and filled with a solid polymer
3.6.3.4
cushioned core rope
rope in which the core is covered (coated), or filled and covered (coated), with a solid polymer, see Figure 22
13
СТБ EN 12385-2-2009
|
|
Figure 22 — Cushioned core rope |
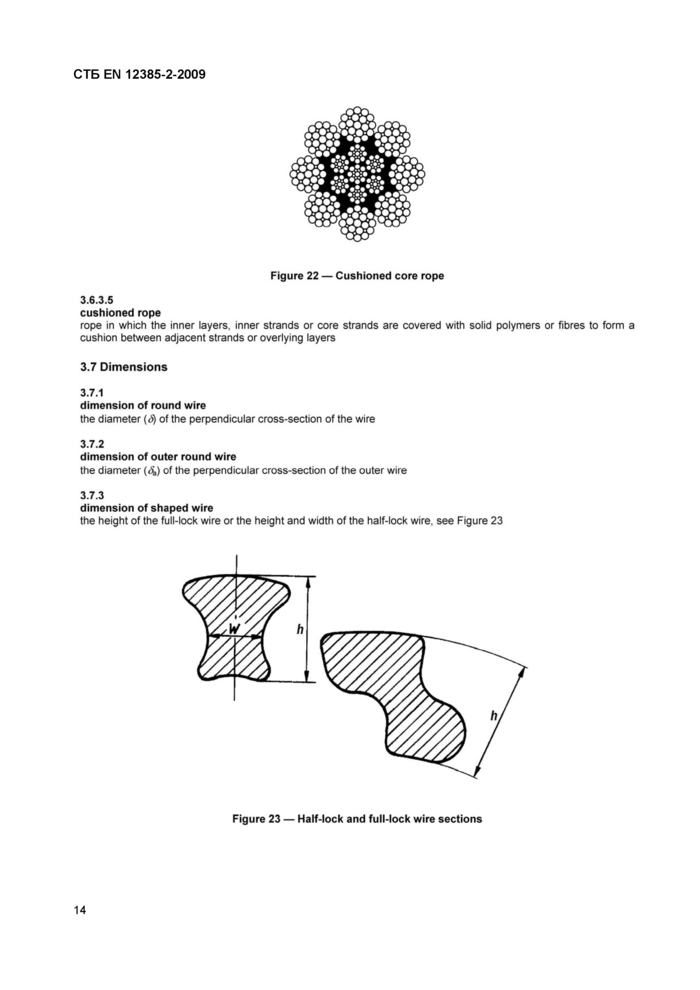
3.6.3.5
cushioned rope
rope in which the inner layers, inner strands or core strands are covered with solid polymers or fibres to form a cushion between adjacent strands or overlying layers
3.7 Dimensions
3.7.1
dimension of round wire
the diameter (S) of the perpendicular cross-section of the wire
3.7.2
dimension of outer round wire
the diameter (4) of the perpendicular cross-section of the outer wire
3.7.3
dimension of shaped wire
the height of the full-lock wire or the height and width of the half-lock wire, see Figure 23
|
|
Figure 23 — Half-lock and full-lock wire sections |
14
СТБ EN 12385-2-2009
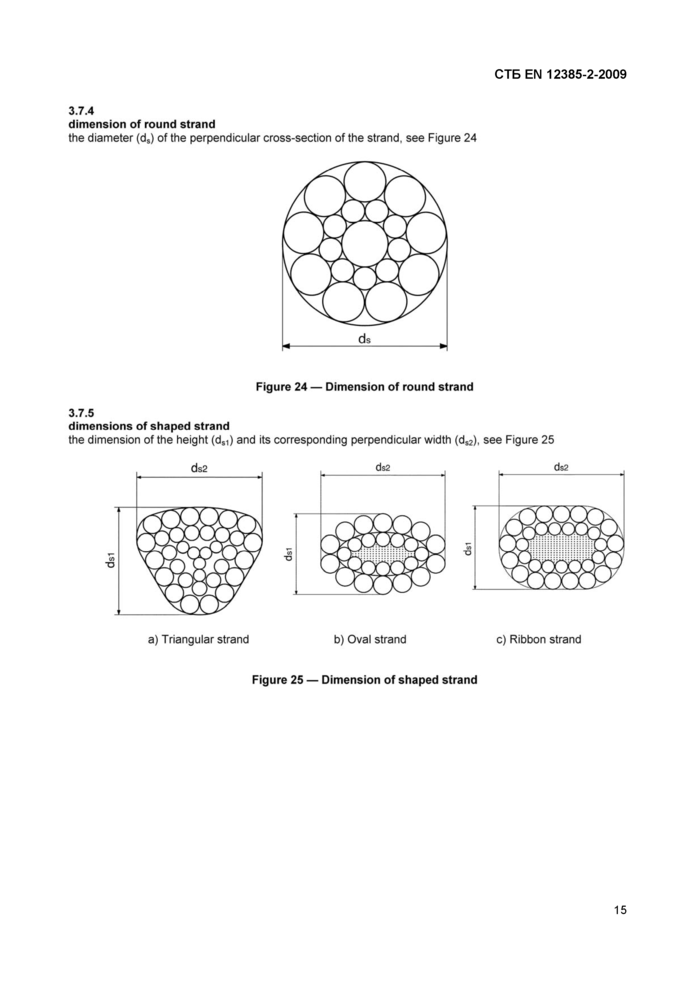
3.7.4
dimension of round strand
the diameter (ds) of the perpendicular cross-section of the strand, see Figure 24
|
|
ds
Figure 24 — Dimension of round strand |
3.7.5
dimensions of shaped strand
the dimension of the height (ds1) and its corresponding perpendicular width (ds2), see Figure 25
|
|
Figure 25 — Dimension of shaped strand |
СТБ EN 12385-2-2009
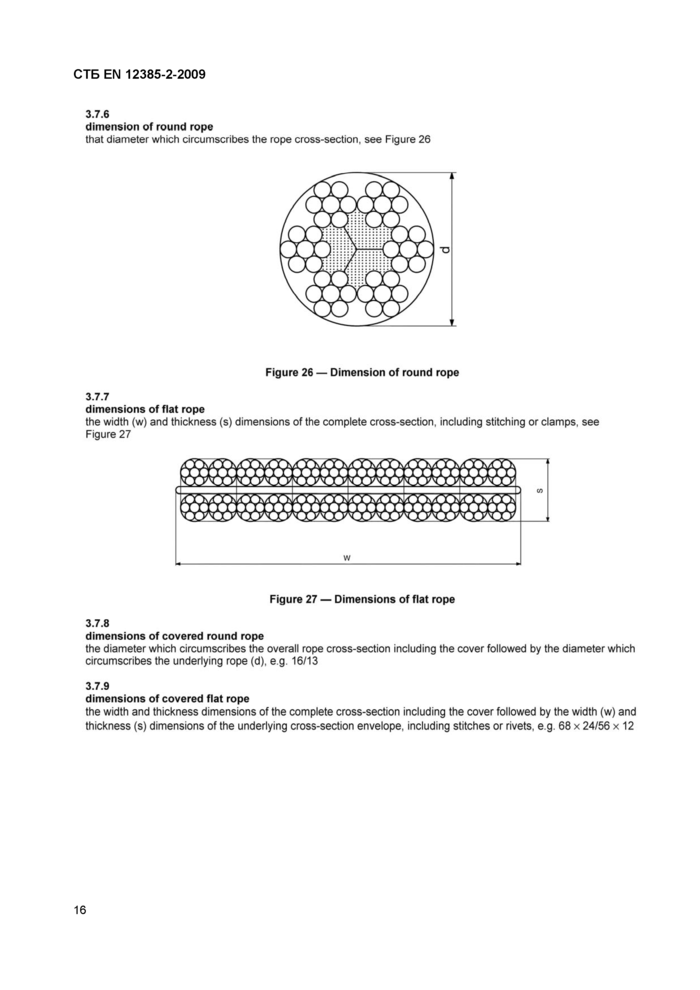
3.7.6
dimension of round rope
that diameter which circumscribes the rope cross-section, see Figure 26
|
|
Figure 26 — Dimension of round rope |
3.7.7
dimensions of flat rope
the width (w) and thickness (s) dimensions of the complete cross-section, including stitching or clamps, see Figure 27
|
|
Figure 27 — Dimensions of flat rope |
3.7.8
dimensions of covered round rope
the diameter which circumscribes the overall rope cross-section including the cover followed by the diameter which circumscribes the underlying rope (d), e g. 16/13
3.7.9
dimensions of covered flat rope
the width and thickness dimensions of the complete cross-section including the cover followed by the width (w) and thickness (s) dimensions of the underlying cross-section envelope, including stitches or rivets, e.g. 68 x 24/56 x 12
16
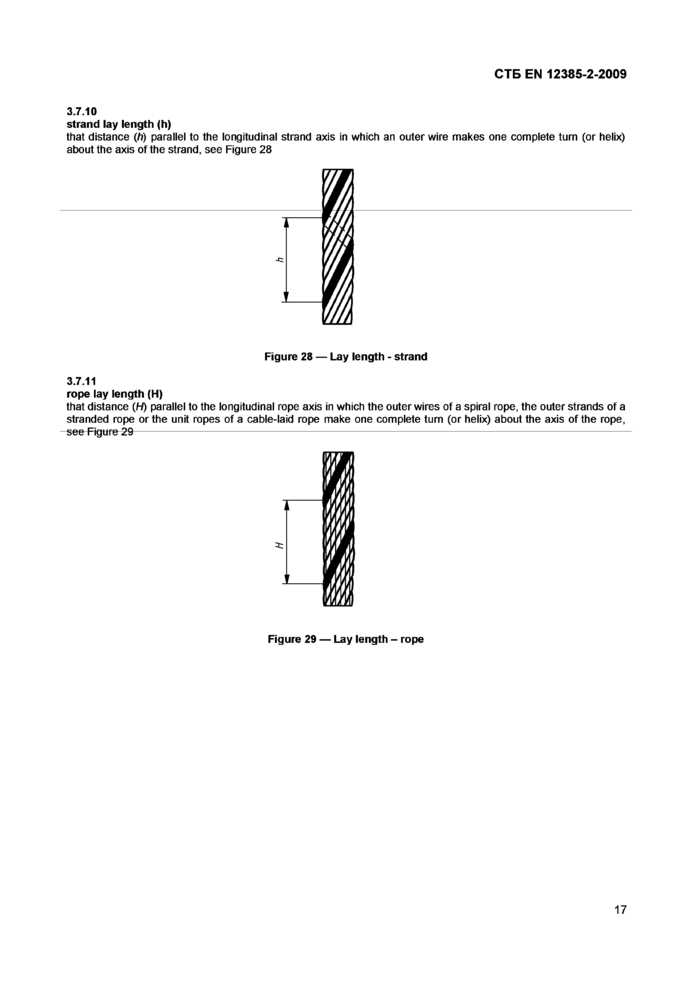
3.7.10
strand lay length (h)
that distance (h) parallel to the longitudinal strand axis in which an outer wire makes one complete turn (or helix) about the axis of the strand, see Figure 28
Figure 28 — Lay length - strand
3.7.11
rope lay length (H)
that distance (H) parallel to the longitudinal rope axis in which the outer wires of a spiral rope, the outer strands of a stranded rope or the unit ropes of a cable-laid rope make one complete turn (or helix) about the axis of the rope, see Figure 29
Figure 29 — Lay length - rope
СТБ EN 12385-2-2009
Введение
Настоящий стандарт содержит текст европейского стандарта EN 12385-2:2002 + А1:2008 на языке оригинала и его перевод на русский язык (справочное приложение Д.А).
Введен в действие как стандарт, на который есть ссылка в Еврокоде EN 1993-1-11:2006.
ГОСУДАРСТВЕННЫЙ СТАНДАРТ РЕСПУБЛИКИ БЕЛАРУСЬ
КАНАТЫ ПРОВОЛОЧНЫЕ СТАЛЬНЫЕ. БЕЗОПАСНОСТЬ Часть 2
Термины и определения, обозначения и классификация
КАНАТЫ ДРАЦЯНЫЯ СТАЛЬНЫЯ.
БЯСПЕКА Частка 2
Тэрмшы i азначэнш, абазначэнш i клааф1кацыя
Steel wire ropes. Safety Part 2
Definitions, designations and classifications
Дата введения 2010-01-01
СТБ EN 12385-2-2009
3.7.12
measured rope length (Lm)
the length which corresponds to the actual length supplied using a prescribed method NOTE The measured length can also be specified at a pre-determined load.
3.7.13
nominal rope length (L)
the length on which the order is usually based
3.7.14
strand clearance (qs)
the distance corresponding to the clearance (gap) between two adjacent strands in the same strand layer
3.7.15
production length of stranded rope
that length of finished rope produced from one loading of the closing machine
3.7.16
production length of spiral rope (spiral strand or locked coil)
that length of finished rope produced from one machine loading of outer wires laid over one continuous length of inner rope
3.8 Lay directions and types
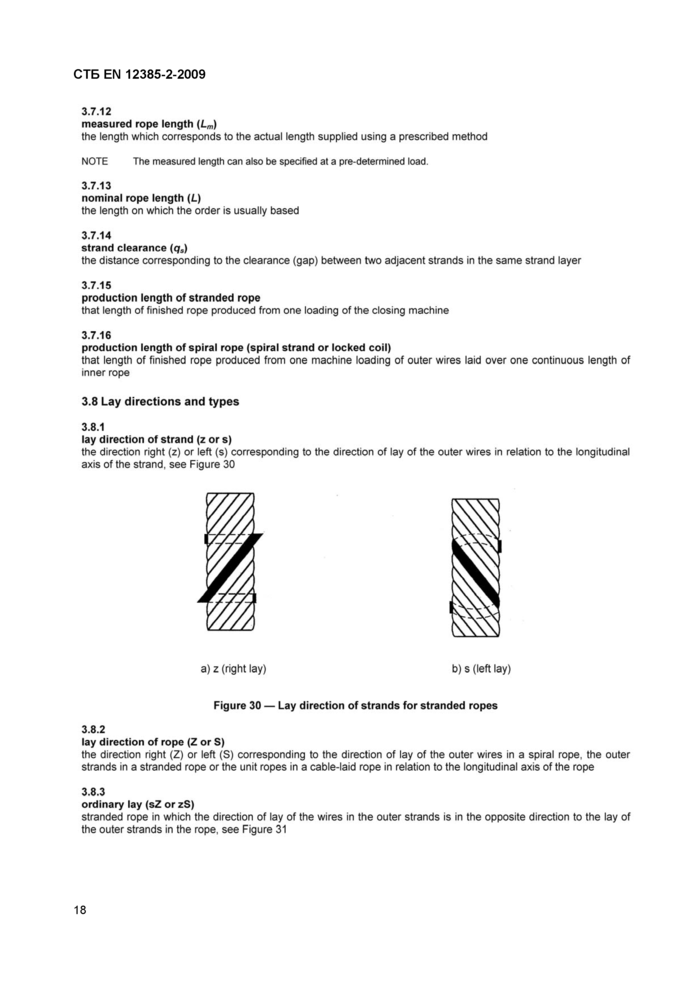
3.8.1
lay direction of strand (z or s)
Figure 30 — Lay direction of strands for stranded ropes
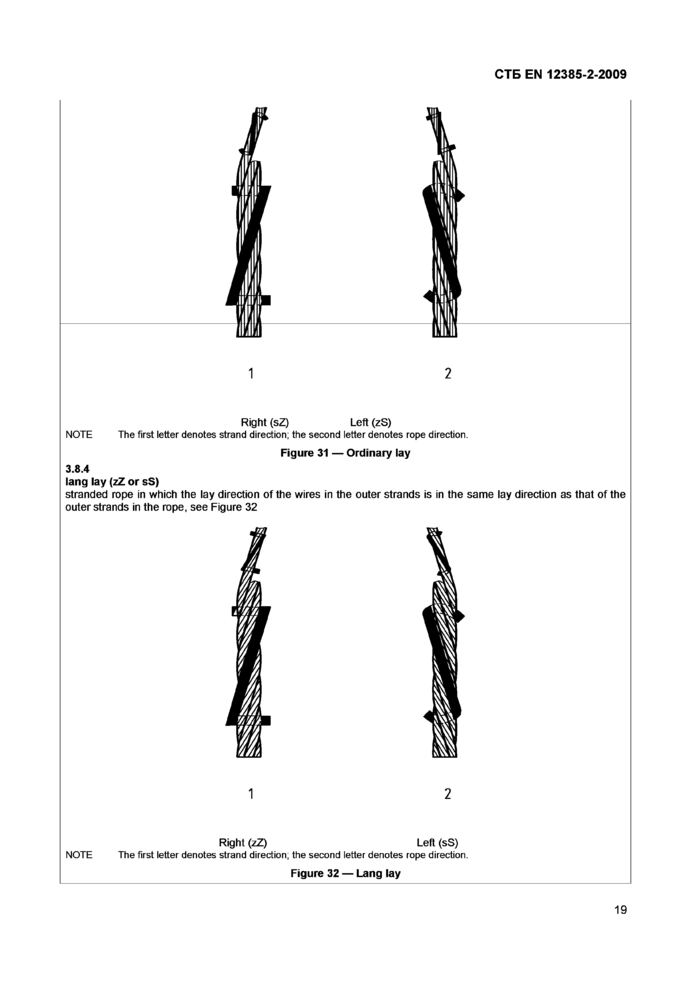
the direction right (z) or left (s) corresponding to the direction of lay of the outer wires in relation to the longitudinal axis of the strand, see Figure 30
3.8.2
lay direction of rope (Z or S)
the direction right (Z) or left (S) corresponding to the direction of lay of the outer wires in a spiral rope, the outer strands in a stranded rope or the unit ropes in a cable-laid rope in relation to the longitudinal axis of the rope
3.8.3
ordinary lay (sZ or zS)
stranded rope in which the direction of lay of the wires in the outer strands is in the opposite direction to the lay of the outer strands in the rope, see Figure 31
18
СТБ EN 12385-2-2009
1 Scope
This part of this European Standard defines terms, specifies designations and classifies steel wire ropes and is for use in conjunction with all other parts of this standard.
It applies to ropes that have been manufactured after the date of issue of the standard.
Not applicable.
3 Terms and definitions
For the purposes of this part of EN 12385, the following terms and definitions apply.
3.1 Wires3.1.1
outer wires
all wires positioned in the outer layer of a spiral rope or in the outer layer of wires in the outer strands of a stranded
rope
3.1.2
inner wires
all wires of intermediate layers positioned between the centre wire and outer layer of wires in a spiral rope or all other wires except centre, filler, core and outer wires in a stranded rope
3.1.3
filler wires
wires used in filler constructions to fill up the interstices between wire layers, see Figure 8
3.1.4
centre wires
wires positioned either at the centre of a spiral rope or the centres of strands of a stranded rope
3.1.5
core wires
all wires of the core of a stranded rope
3.1.6
load-bearing wires
those wires in a rope which are regarded as contributing towards the breaking force of the rope
1
3.1.7
layer of wires
an assembly of wires having one pitch circle diameter. The exception is Warrington layer comprising large and small wires where the smaller wires are positioned on a larger pitch circle diameter than the larger wires. The first layer is that which is laid immediately over the strand centre
NOTE Filler wires do not constitute a separate layer.
3.1.8
stitching wire or strand
single wire or strand used for the stitching of flat ropes
3.1.9
serving wire or strand
single wire or strand used for making a close-wound helical serving to retain the elements of a rope in their assembled position
3.1.10
wire tensile strength grade (R)
a level of requirement of tensile strength of a wire and its corresponding range. It is designated by the value according to the lower limit of tensile strength and is used when specifying wire and when determining the calculated minimum breaking force or calculated minimum aggregate breaking force of a rope, expressed in N/mm2
3.1.11
wire tensile strength (Rm)
the ratio between the maximum force obtained in a tensile test and the nominal cross-sectional area of the test piece, expressed in N/mm2
3/1.12
finish and quality of coating
the condition of the surface finish of the wire e.g. uncoated (bright), zinc coated, zinc alloy coated or other protective coating and the class of coating, e.g. class В zinc coating, defined by the minimum mass of coating and the adherence of the coating to the steel below
3.1.13
mass of coating
the mass of coating (obtained by a prescribed method) per unit of surface area of the uncoated wire, expressed in g/m2
3.2 Strand types
3.2.1
strand
an element of rope consisting of an assembly of wires of appropriate shape and dimensions laid helically in the same direction in one or more layers around a centre
NOTE Strands containing three or four wires in the first layer, or certain shaped strands (e.g. ribbon) cannot have a centre.
2
СТБ EN 12385-2-2009
3.2.2
round strand
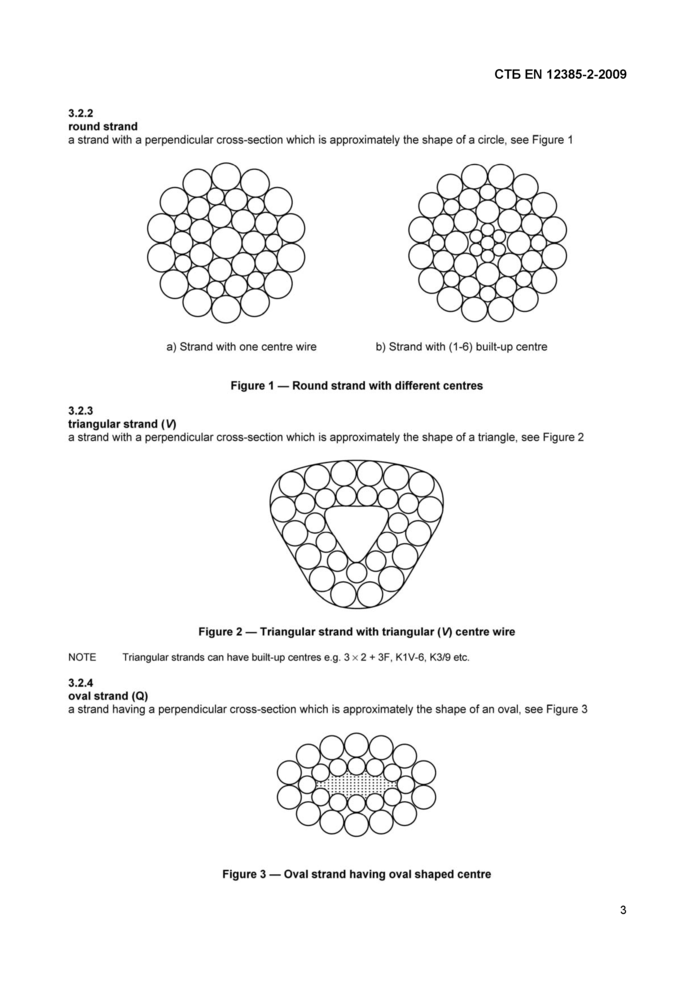
a strand with a perpendicular cross-section which is approximately the shape of a circle, see Figure 1
b) Strand with (1-6) built-up centre
Figure 1 — Round strand with different centres
3.2.3
triangular strand (V)
|
|
Figure 2 — Triangular strand with triangular (V) centre wire |
a strand with a perpendicular cross-section which is approximately the shape of a triangle, see Figure 2
NOTE Triangular strands can have built-up centres e.g. 3 x 2 + 3F, K1V-6, K3/9 etc.
3.2.4
oval strand (Q)
|
|
Figure 3 — Oval strand having oval shaped centre |
a strand having a perpendicular cross-section which is approximately the shape of an oval, see Figure 3
3
СТБ EN 12385-2-2009
3.2.5
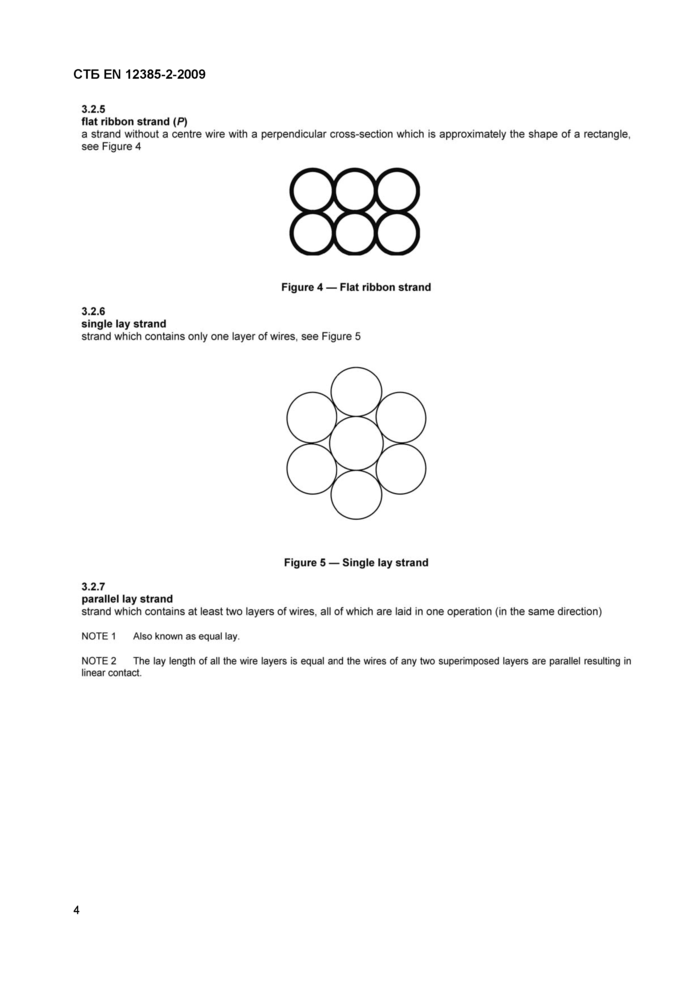
flat ribbon strand (P)
a strand without a centre wire with a perpendicular cross-section which is approximately the shape of a rectangle, see Figure 4
|
|
Figure 4 — Flat ribbon strand |
3.2.6
single lay strand
strand which contains only one layer of wires, see Figure 5
|
|
Figure 5 — Single lay strand |
3.2.7
parallel lay strand
strand which contains at least two layers of wires, all of which are laid in one operation (in the same direction)
NOTE 1 Also known as equal lay.
NOTE 2 The lay length of all the wire layers is equal and the wires of any two superimposed layers are parallel resulting in linear contact.
4
СТБ EN 12385-2-2009
3.2.8
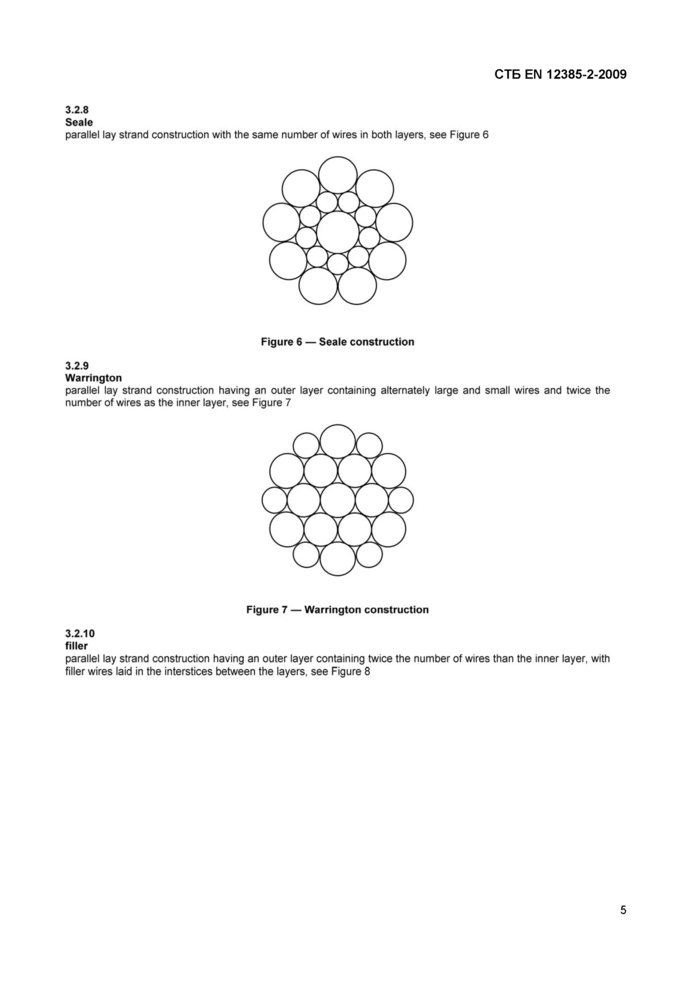
Seale
parallel lay strand construction with the same number of wires in both layers, see Figure 6
|
|
Figure 6 — Seale construction |
3.2.9
Warrington
parallel lay strand construction having an outer layer containing alternately large and small wires and twice the number of wires as the inner layer, see Figure 7
|
|
Figure 7 — Warrington construction |
3.2.10
filler
parallel lay strand construction having an outer layer containing twice the number of wires than the inner layer, with filler wires laid in the interstices between the layers, see Figure 8
5
СТБ EN 12385-2-2009
|
|
Figure 8 — Filler construction |
3.2.11
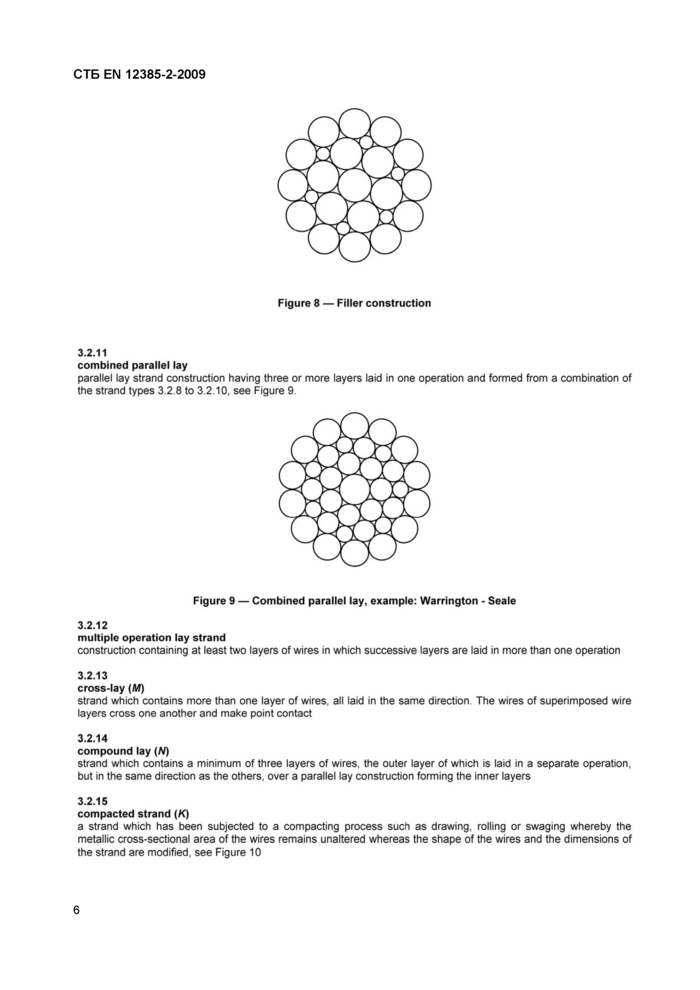
combined parallel lay
parallel lay strand construction having three or more layers laid in one operation and formed from a combination of the strand types 3.2.8 to 3.2.10, see Figure 9.
|
|
Figure 9 — Combined parallel lay, example: Warrington - Seale |
3.2.12
multiple operation lay strand
construction containing at least two layers of wires in which successive layers are laid in more than one operation
3.2.13
cross-lay (M)
strand which contains more than one layer of wires, all laid in the same direction. The wires of superimposed wire layers cross one another and make point contact
3.2.14
compound lay (N)
strand which contains a minimum of three layers of wires, the outer layer of which is laid in a separate operation, but in the same direction as the others, over a parallel lay construction forming the inner layers
3.2.15
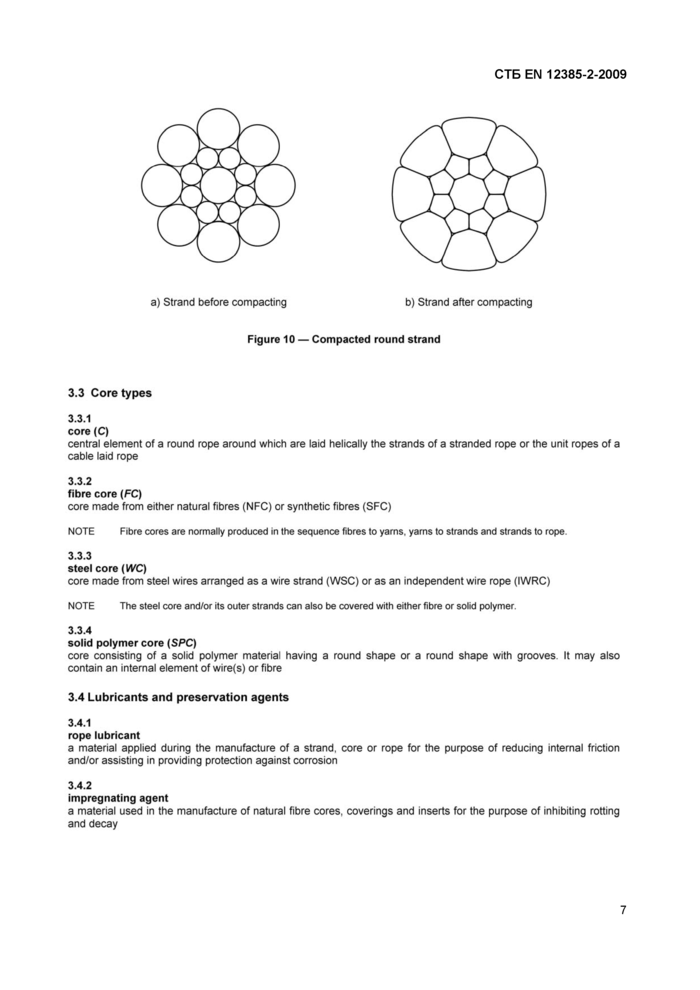
compacted strand (K)
a strand which has been subjected to a compacting process such as drawing, rolling or swaging whereby the metallic cross-sectional area of the wires remains unaltered whereas the shape of the wires and the dimensions of the strand are modified, see Figure 10
6
СТБ EN 12385-2-2009
a) Strand before compacting
b) Strand after compacting
Figure 10 — Compacted round strand
3.3 Core types
3.3.1 core (C)
central element of a round rope around which are laid helically the strands of a stranded rope or the unit ropes of a cable laid rope
3.3.2
fibre core (FC)
core made from either natural fibres (NFC) or synthetic fibres (SFC)
NOTE Fibre cores are normally produced in the sequence fibres to yarns, yarns to strands and strands to rope.
3.3.3
steel core (WC)
core made from steel wires arranged as a wire strand (WSC) or as an independent wire rope (IWRC)
NOTE The steel core and/or its outer strands can also be covered with either fibre or solid polymer.
3.3.4
solid polymer core (SPC)
core consisting of a solid polymer material having a round shape or a round shape with grooves. It may also contain an internal element of wire(s) or fibre
3.4 Lubricants and preservation agents
3.4.1
rope lubricant
a material applied during the manufacture of a strand, core or rope for the purpose of reducing internal friction and/or assisting in providing protection against corrosion
3.4.2
impregnating agent
a material used in the manufacture of natural fibre cores, coverings and inserts for the purpose of inhibiting rotting and decay